In the world of construction, effective project management hinges on accurate planning and scheduling. A well-structured schedule ensures that projects are completed on time and according to quality standards. Construction scheduling involves organizing tasks, allocating resources, and setting deadlines for each phase of a project. Among the various techniques available for scheduling, the Critical Path Method (CPM) stands out as one of the most widely used and effective approaches.
Understanding CPM is essential for construction project managers because it helps them identify the most crucial tasks, known as “critical” activities, which directly impact the project’s completion time. By focusing on these critical tasks, project managers can better allocate resources, avoid delays, and keep the project on track. Whether managing small-scale builds or large, complex infrastructure projects, CPM scheduling offers a roadmap to success, making it a vital tool in construction project management.
What is the Critical Path Method (CPM)?
The Critical Path Method (CPM) is a project management technique used to identify the longest sequence of dependent activities required to complete a project. This sequence is known as the “critical path,” and it determines the shortest possible time needed to finish the project. In simple terms, the critical path consists of the tasks that must be completed on time for the project to meet its overall deadline. If any task on the critical path is delayed, the entire project will be delayed.
How to create a CPM Schedule?

- List All Project Activities
Start by identifying all the tasks or activities required to complete the construction project. These activities can range from Preconstruction, followed by Construction phases such as Site Preparation, Infrastructure, Super Structure, MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing), and Finishes, and finally, the Closeout phase. Each activity should be clearly defined and detailed. - Determine Dependencies Between Activities
Establish the relationships between activities, identifying which tasks depend on others. For example, you cannot start installing windows until the walls have been erected. Dependence helps in determining the sequence of tasks and which ones must be completed before others can begin. - Estimate Durations for Each Activity
Assign a realistic time duration to each task. This involves estimating how long each activity will take, considering factors like labor, materials, and equipment availability. Accurate time estimation is crucial for a reliable schedule. - Identify the Critical Path
Once you have all the activities, their dependencies, and durations, you can determine the critical path. The critical path is the longest chain of dependent tasks, and it represents the shortest time in which the entire project can be completed. Any delay in activities on the critical path will directly delay the project’s completion. - Monitor and Update the CPM Schedule
Throughout the construction project, regularly monitor progress and update the schedule as needed. Changes in scope, unexpected delays, or faster-than-expected progress can affect the critical path, so it’s important to adjust the plan in real time.
How CPM Helps in Project Efficiency, Deadlines, and Resource Management
- Enhancing Project Efficiency
CPM improves project efficiency by breaking down the project into manageable tasks and identifying their dependencies. This clear structure allows for streamlined execution, minimizing wasted effort and ensuring that tasks are completed in the right sequence. Additionally, CPM highlights tasks that can be completed simultaneously, further accelerating project progress. - Meeting Deadlines
The critical path directly impacts the project’s timeline. By focusing on the critical path, project managers can ensure that key tasks are completed on schedule, reducing the risk of project delays. CPM also allows for real-time adjustments, helping teams stay on track even when unexpected changes arise. - Optimizing Resource Management
Effective resource management is a crucial component of any construction project. CPM helps allocate resources to the most important tasks, preventing overuse or underutilization of labor, equipment, and materials. By prioritizing critical activities, resources are used more effectively, leading to cost savings and improved productivity.
CPM Scheduling vs. Other Construction Scheduling Techniques
When it comes to construction scheduling, various techniques are used to plan, track, and execute projects. Among the most popular are the Critical Path Method (CPM), Gantt charts, and Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT). While these techniques share some similarities, each has unique strengths and applications in construction project management. Understanding their differences can help project managers choose the most appropriate tool for their needs.
CPM vs. Gantt Charts
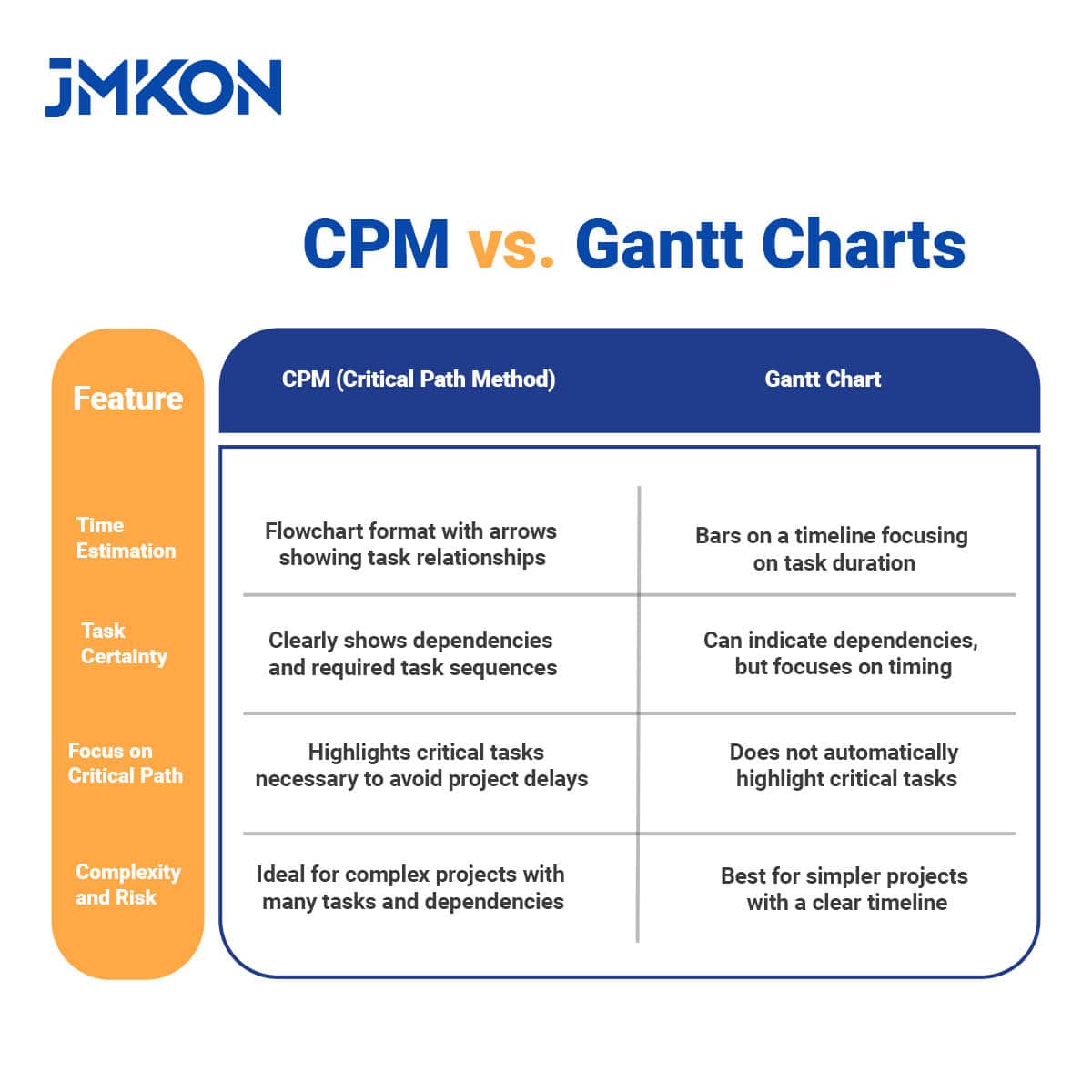
Time Estimation
- CPM (Critical Path Method): Flowchart format with arrows showing task relationships.
- Gantt Chart: Bars on a timeline focusing on task duration.
Task Certainty
- CPM (Critical Path Method): Clearly shows dependencies and required task sequences.
- Gantt Chart: Can indicate dependencies, but focuses on timing.
Focus on Critical Path
- CPM (Critical Path Method): Highlights critical tasks necessary to avoid project delays.
- Gantt Chart: Does not automatically highlight critical tasks.
Complexity and Risk
- CPM (Critical Path Method): Ideal for complex projects with many tasks and dependencies.
- Gantt Chart: Best for simpler projects with a clear timeline.
CPM vs. PERT
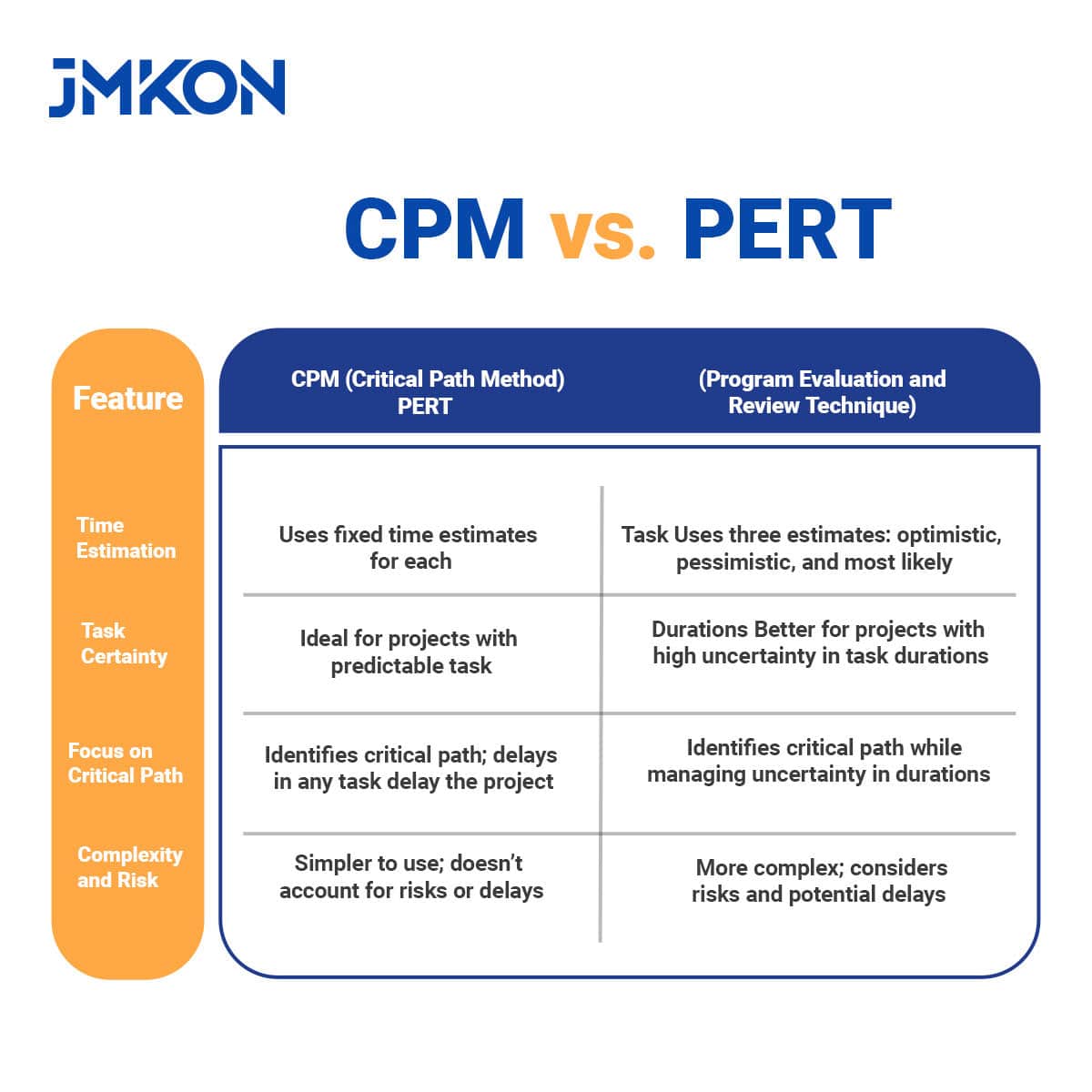
Time Estimation:
- CPM: Uses fixed time estimates for each task, assuming you know how long each will take.
- PERT: Uses three-time estimates (optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely) to account for uncertainty in how long tasks will take.
Task Certainty:
- CPM: Great for projects where you can accurately predict how long tasks will take.
- PERT: Better for projects with a lot of uncertainty, where you’re unsure how long tasks might take.
Focus on Critical Path:
- CPM: Identifies the critical path (the most important sequence of tasks), and if one is delayed, the whole project gets delayed.
- PERT: Focuses on managing uncertainty in task durations, but still identifies the critical path.
Complexity and Risk:
- CPM: Simpler for projects with predictable tasks and doesn’t consider risks like delays.
- PERT: More complex because it accounts for risk and uncertainty, making it useful when you need to predict potential delays.
Choosing the Right Scheduling Technique
Both CPM and Gantt charts offer valuable insights for construction project management, but CPM provides a more detailed view of task dependencies and critical activities, making it ideal for complex projects. Meanwhile, Gantt charts offer a simpler, more visual representation of the project’s timeline, better suited for less complex tasks.
When comparing CPM and PERT, CPM’s fixed time estimates make it suitable for construction projects where durations are predictable, while PERT’s probabilistic approach is more useful in projects with greater uncertainty. Understanding the differences between these methods helps project managers select the best scheduling technique based on the specific needs of their project.
Benefits of Using CPM Scheduling in Large Construction Projects

The Critical Path Method (CPM) is especially beneficial in large construction projects due to the complex nature of managing multiple tasks, teams, and resources.
CPM provides a structured approach that helps project managers ensure timely completion, better resource allocation, and effective team coordination. Here are some key benefits of using CPM in large-scale construction projects:
How CPM Reduces Project Delays
One of the primary advantages of CPM is its ability to minimize project delays. By identifying the critical path, project managers can pinpoint the tasks that must be completed on time to avoid delays in the overall schedule. This allows for better planning and resource allocation to ensure these critical tasks stay on track.
- Proactive Delay Management:
CPM enables project managers to foresee potential bottlenecks and delays by focusing on critical tasks. If one task on the critical path is behind schedule, managers can take immediate action, such as reallocating resources or adjusting other tasks to make up for lost time.
Ensuring Better Coordination Among Teams
Large construction projects often involve multiple teams working on different tasks simultaneously. CPM scheduling ensures better coordination among these teams by providing a clear, organized timeline of activities and dependencies.
- Improved Communication:
CPM visually maps out the sequence of tasks, helping teams understand the flow of work and when their tasks need to be completed. Teams can see how their work fits into the overall project and how delays or early completion affect other teams. - Efficient Resource Allocation:
By tracking the progress of critical tasks, project managers can allocate resources (labor, equipment, materials) where they are needed the most. This helps avoid situations where one team is idle while waiting for another team to finish its work.
Popular CPM Scheduling Software Tools for Construction Management
In today’s construction industry, using the right software is essential for effectively managing the complex schedules and tasks involved in large projects. Several tools specialize in Critical Path Method (CPM) scheduling, helping construction managers streamline their workflows, track progress, and optimize resource allocation. Below is an overview of some of the top CPM scheduling software options and the key features you should look for when choosing a tool for your project.
Top CPM Software
- Primavera P6 (by Oracle)
Primavera P6 is one of the most widely used CPM scheduling tools in large construction projects.
- Microsoft Project
Microsoft Project is a versatile project management tool used across many industries, including construction.
- Asta Powerproject
Asta Powerproject is a popular CPM scheduling tool, especially in Europe, known for its ease of use and powerful scheduling features.
- Procore
Procore is an all-in-one construction management platform that includes CPM scheduling, alongside tools for project collaboration, document management, and budgeting.
- Tilos
Tilos is a CPM scheduling tool that focuses on linear scheduling, which is particularly useful for infrastructure projects like roads, railways, and pipelines.
The Critical Path Method (CPM) has proven to be a vital tool for managing construction projects of all sizes and complexities. CPM scheduling allows project managers to plan, execute, and monitor construction tasks efficiently, ensuring that projects are completed on time, within budget, and according to specified quality standards. Here’s a recap of the key takeaways and a look at future trends in CPM scheduling for construction projects.




