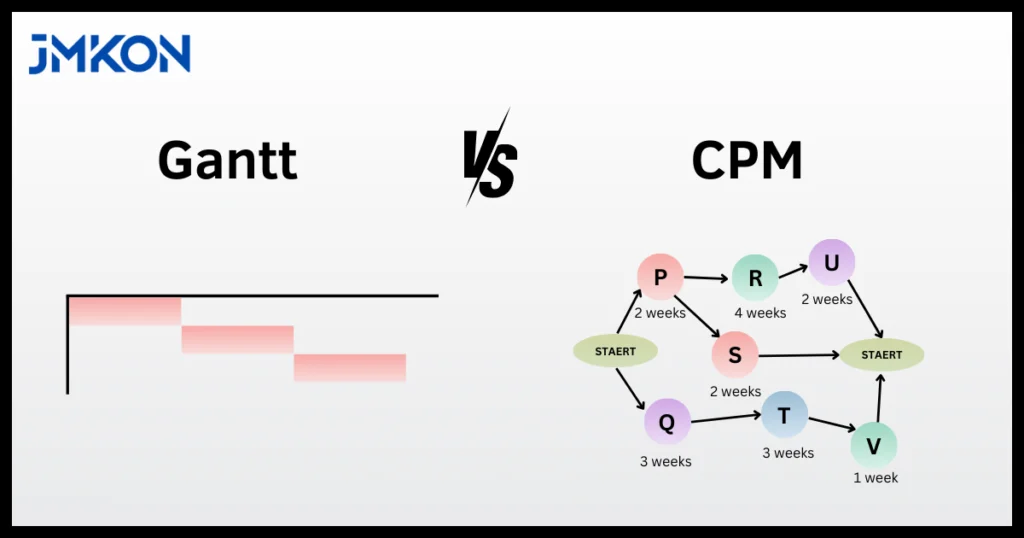
The Gantt chart and Critical Path Method (CPM) are two of the most powerful tools in project management, offering distinct ways to plan, track, and execute projects effectively. In an era where time and resources are precious, these tools help teams navigate complexities, ensuring that deadlines are met and goals are achieved.
A Gantt chart paints the big picture, showcasing tasks, timelines, and milestones in a visually intuitive way. On the other hand, the Critical Path Method dives deeper, identifying the sequence of tasks that are crucial to a project’s success. While both tools are indispensable, understanding their differences is the first step to selecting the right approach for your unique challenges.
In this article, we’ll break down the difference between Gantt charts and the Critical Path Method, helping you decide which tool fits your needs. At JMKON, we specialize in providing expert CPM services to ensure your most complex projects are delivered with precision and confidence.
What Are Gantt Chart and the Critical Path Method?
Here’s the difference between Gantt chart and critical path method:
Defining Gantt Charts

A Gantt chart is one of the most widely recognized tools in project management, known for its simplicity and visual clarity. This tool uses a bar chart format to map out tasks against a timeline, offering an intuitive way to plan, schedule, and track progress.
Each bar on a Gantt chart represents a task, showing its start and end dates and illustrating how tasks overlap or depend on each other. With its straightforward structure, a Gantt chart is ideal for projects where visibility and team collaboration are key. Commonly used in industries like marketing, event planning, and construction, it’s an indispensable tool for tracking milestones and staying on top of deadlines.
Explaining the Critical Path Method

The Critical Path Method (CPM) takes a more analytical approach to project management. CPM focuses on identifying the sequence of tasks that directly impact the project’s completion date. This sequence, known as the “critical path,” highlights tasks that must be completed on time to avoid delays.
Unlike a Gantt chart, which emphasizes timelines, CPM delves into task dependencies and durations to calculate the shortest possible project timeline. By identifying which activities are critical and which have flexibility (float), CPM allows project managers to allocate resources strategically and anticipate potential bottlenecks. It’s particularly valuable for complex projects where precision and efficiency are non-negotiable.
Visual Representation: Gantt Charts vs Critical Path Method
Gantt Charts as Visual Tools
- Timeline-Based Design
A Gantt chart and Critical Path Method both play crucial roles in project management, but the Gantt chart excels in visual simplicity. It uses horizontal bars on a timeline to represent tasks. Each bar’s length indicates task duration, and its placement on the timeline shows when tasks begin and end. - Clear, Visual Overview
The Gantt chart offers a clear visual representation of the entire project, making it easy to understand the flow of tasks and milestones at a glance. This is particularly useful for tracking project timelines and ensuring that deadlines are met. - Task Dependencies
- Dependencies between tasks are shown using arrows.
- For example, Task A must be completed before Task B can start, and the arrow visually indicates this order in the timeline.
- Example Use Case:
In a marketing campaign, the Gantt chart might show tasks like “Market Research” followed by “Content Creation,” with an arrow indicating that content creation cannot begin until the research phase is completed.
CPM’s Analytical Diagrams
- Network-Based Design
The Critical Path Method relies on network diagrams rather than a simple timeline. In these diagrams, tasks are represented as nodes (or boxes), and arrows between them indicate dependencies. This is where the Gantt chart and Critical Path Method differ significantly in approach. - Critical Path Identification
One of the key features of CPM is the identification of the critical path. The critical path represents the longest sequence of dependent tasks, and delays in these tasks will push back the project’s completion date. The Critical Path Method is highly effective in pinpointing these essential tasks. - Task Dependencies
- Dependencies in CPM are more intricate than in Gantt charts, as CPM deals with complex relationships between tasks.
- CPM identifies which tasks must be completed on time to avoid delaying the entire project, giving project managers the ability to allocate resources efficiently.
- Example Use Case:
For a large construction project, the Critical Path Method would show that “Excavation” needs to be finished before “Foundation” can begin, and “Foundation” must be completed before “Framing” starts. CPM highlights which tasks are critical to maintaining the project timeline.
Key Differences Between Gantt Charts and the Critical Path Method
Primary Focus of Each Tool
- Gantt Chart Focus: Scheduling and Visualization
- The Gantt chart and Critical Path Method serve different core functions in project management. The Gantt chart focuses primarily on scheduling. It offers a visual representation of tasks along a timeline, allowing project managers to easily see the project’s progress, upcoming deadlines, and how tasks overlap.
- It’s perfect for managing time, resources, and milestones in projects where clear scheduling is the priority.
- CPM Focus: Task Dependencies and Optimization
- The Critical Path Method, on the other hand, focuses more on the relationships between tasks. It identifies task dependencies and highlights the critical path—the sequence of tasks that directly impact the project’s completion.
- CPM is ideal for projects where understanding the interdependencies and the critical tasks is crucial to avoiding delays.
Levels of Complexity
- Simple Projects: Best for Gantt Charts
- Gantt charts are well-suited for simple projects with fewer interdependencies. They provide a straightforward way to visualize tasks and timelines. The simplicity of Gantt charts makes them effective in scenarios where task scheduling is the primary concern, and task interdependencies are minimal.
- Example: A small event planning project where tasks like venue booking, catering, and invitations have clear and simple timelines.
- Complex Projects: Best for CPM
- For complex projects involving multiple tasks with intricate dependencies, the Critical Path Method is more effective. CPM helps identify which tasks must be prioritized to avoid delays, making it essential for large-scale projects with overlapping tasks and time constraints.
- Example: A construction project where tasks such as excavation, foundation, and framing depend heavily on one another.
Key Strengths and Applications
- Strengths of Gantt Charts
- Clarity: Gantt charts provide an easy-to-understand visual of project tasks and timelines.
- Task Tracking: They help track task progress and identify potential delays in real time.
- Applications: Ideal for smaller projects, event planning, or any situation where timeline visualization is key.
- Strengths of CPM
- Critical Path Identification: CPM’s strength lies in its ability to identify critical tasks that affect the project’s completion date.
- Optimization: It helps in allocating resources efficiently and minimizing delays by focusing on critical activities.
- Applications: Best suited for complex projects in industries like construction, IT, and large-scale manufacturing, where task dependencies play a pivotal role in project success.
When to Use Gantt Charts vs. the Critical Path Method in Your Project

A Gantt chart and Critical Path Method serve distinct purposes, but Gantt charts are perfect for projects that are simple and timeline-driven. These charts provide a clear visual layout that helps managers and teams track tasks in a linear fashion.
Examples of Projects Where Gantt Charts Excel:
- Marketing Campaigns
A Gantt chart is ideal when tasks like “content creation,” “social media posting,” and “email marketing” need to be completed in a certain order but do not have a complex dependency structure. The Gantt chart visually shows when each task starts and ends, making it easy to keep things on track. - Event Planning
Events require a well-defined timeline, where tasks such as booking venues, organizing guest lists, and preparing marketing materials must be completed on time. A Gantt chart is an excellent tool for visualizing and managing this schedule.
Why Use Gantt Charts?
- Collaboration Made Easy: The Gantt chart is an intuitive tool that simplifies collaboration among teams. Everyone can clearly see deadlines and tasks, which enhances communication and reduces misunderstandings.
- Tracking Milestones: With a Gantt chart, tracking the completion of milestones becomes easy, ensuring that each task is completed before the next one begins.
For smaller projects or when the focus is primarily on timelines and task visibility, Gantt charts are a perfect solution. They help avoid confusion and ensure that all team members are on the same page.
Scenarios Ideal for CPM
While Gantt charts are great for straightforward projects, the Critical Path Method comes into play when tasks become more complex and depend on each other. CPM helps to manage projects where delays in specific tasks can significantly affect the overall timeline.
Why Choose CPM for Complex Projects?
The Critical Path Method is perfect for complex projects that involve a large number of interdependent tasks. Here’s why:
- Task Dependencies and Precision
CPM is designed to map out task dependencies in detail. For example, in a construction project, the completion of the foundation is crucial before framing can start. CPM helps project managers identify which tasks are critical and should be prioritized. - Resource Optimization
CPM also aids in resource management. By highlighting the critical path, it helps managers allocate resources more efficiently to avoid delays and maximize project success.
Example Use Cases:
- Construction Projects
When building a multi-story building, CPM allows managers to see exactly where delays in the foundation or roofing could push back the completion date. It’s essential to know which tasks must be completed first and which can be delayed. - IT Development Projects
In construction scheduling software development, CPM allows teams to see how delays in one module (e.g., back-end development) can affect the entire system rollout. It helps in assigning critical resources where they are needed most.
Pros and Cons: Gantt Charts vs Critical Path Method
Advantages and Disadvantages of Gantt Charts
Here are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Gantt Charts:
Advantages of Gantt Charts
- Ease of Use: The Gantt chart and Critical Path Method serve different purposes, but Gantt charts are highly user-friendly. With simple bar charts, project managers and teams can easily visualize timelines, task durations, and milestones.
- Quick Overview: A Gantt chart provides a clear, visual overview of the entire project. It’s especially helpful in smaller projects or when you need a quick snapshot of what’s happening and when.
- Effective for Collaboration: Since Gantt charts are straightforward and visual, they promote collaboration by making it easy for team members to see what’s ahead and how they need to work together.
- Time Management: It’s a great tool for tracking when tasks need to start and end. Gantt charts help managers maintain project schedules, ensuring tasks are completed on time.
Disadvantages of Gantt Charts
- Limited Dependency Tracking: The biggest drawback of a Gantt chart is that it doesn’t track task dependencies as effectively as CPM. While dependencies are shown through arrows, they lack the depth needed for complex projects.
- Can Get Cluttered: As the project grows and the number of tasks increases, the Gantt chart can become cluttered and difficult to read, especially for larger, more complex projects.
- Not Ideal for Complex Projects: For large-scale projects with multiple interdependent tasks, Gantt charts can lack the precision required for CPM scheduling services and resource management.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CPM
Here are the Advantages and Disadvantages of CPM:
Advantages of the Critical Path Method (CPM)
- Task Dependency Analysis: CPM excels in identifying task dependencies. By focusing on the critical path, it shows how tasks are linked and which ones must be completed on time to avoid delaying the entire project.
- Resource Allocation: One of the biggest strengths of CPM is its ability to optimize resource allocation. It highlights critical tasks, enabling project managers to allocate resources where they are needed most, minimizing downtime and maximizing efficiency.
- Precision in Large Projects: In projects with many tasks and dependencies, CPM provides a level of detail and precision that Gantt charts can’t offer. This is especially beneficial for complex, multi-phase projects like construction, IT development, or large-scale manufacturing.
Disadvantages of the Critical Path Method (CPM)
- Complex Setup: The biggest challenge with CPM is its complexity during setup. Developing the network diagram and identifying the critical path requires more effort and detailed planning than simply plotting a Gantt chart.
- Requires Detailed Data: To accurately use CPM, you need detailed information on task durations, dependencies, and resources. Incomplete or inaccurate data can undermine the effectiveness of the method.
- Harder to Collaborate: While CPM is excellent for precise project planning, it’s not as intuitive or easy to share with non-project management team members. It may require more explanation compared to the Gantt chart’s visual format.
To sum it up, Gantt charts are perfect for straightforward project timelines, while the Critical Path Method (CPM) shines when managing complex projects with interdependent tasks. Choosing the right tool depends on your project’s needs—use Gantt charts for simplicity and CPM for precision.
At JMKON, we specialize in CPM services that ensure your complex projects stay on track. Let us help you navigate your project’s critical path and achieve success on time, every time.