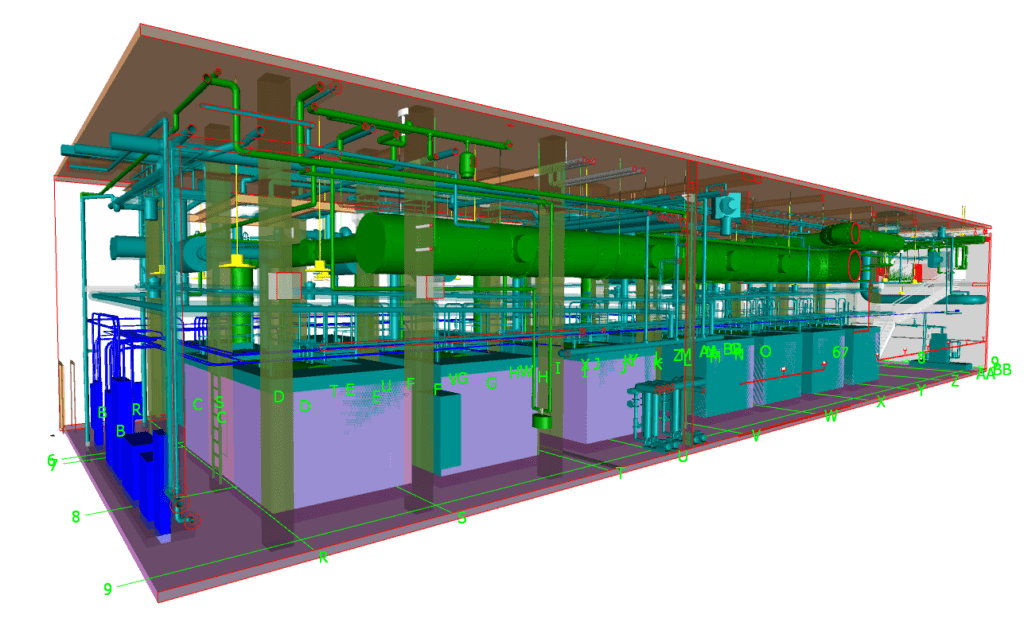
At JMKON LLC, we prioritize using advanced strategies to ensure the success of our construction projects. such strategy is the Federation Strategy in BIM, This blog explains the importance of using a Federation Strategy in BIM, making it easy to understand its benefits.
What is a Federation Strategy in BIM?
A Federation Strategy in BIM involves combining multiple models created by different disciplines (such as architecture, structural engineering, and MEP) into a single, comprehensive model. Each discipline maintains its own model, but these are brought together to ensure coordination and integration across the project.
Key Benefits of a Federation Strategy in BIM

1. Enhanced Coordination
- Reduced clashes: The federated BIM model helps Identifies and resolves conflicts between different models early in the design phase.
- Improved communication: Ensures all teams are working with aligned models, enhancing collaboration.
2. Increased Efficiency
- Streamlined workflows: Facilitates efficient management of various project aspects by integrating models.
- Reduced rework: Minimizes the need for rework by catching issues early in the design process.
3. Better Quality Control
- Consistent standards: Ensures that all models adhere to the same quality standards.
- Thorough reviews: Enables comprehensive review and validation of the integrated model.
4. Effective Project Management
- Improved tracking: Allows for better tracking of progress across different disciplines.
- Enhanced decision-making: Provides a holistic view of the project, aiding in more informed decision-making.
5. Cost Savings
- Early issue detection: Saves costs by identifying and addressing issues before construction begins.
- Optimized resource use: Ensures resources are used efficiently, reducing waste.
Learn more about: Advantages of building information modeling
BIM Federated Model Process
The BIM federated model process involves integrating discipline-specific models, such as architectural, structural, and mechanical models, into a single coordinated framework. This allows each discipline to focus on its specific needs, while the federated model brings everything together to ensure full project alignment.
Discipline Segregation
Each discipline—architecture, structure, and mechanical—develops its own model. For example:
- Architecture Models focus on layouts and aesthetics.
- Structural Models (e.g., concrete or steel) focus on the building’s load-bearing components.
- Mechanical Models include systems like HVAC, plumbing, and electrical.
Sub-discipline segregation
Such as concrete vs. steel structure models, helps refine project details and ensure accuracy. This level of segmentation improves organization and reduces the risk of errors in design and construction.
BIM Federation Techniques for Efficient Collaboration
In large projects, efficient collaboration is essential. BIM federation techniques ensure that contributions from Task Teams, in-house teams, and sub-consultants are organized and seamlessly integrated into the federated model. These techniques allow for real-time collaboration, preventing bottlenecks and ensuring all models align with project objectives.
Contributions from Task Teams and Sub-Consultants
Each team, whether internal or external, develops its segment of the project. Sub-consultants, such as facade or HVAC experts, contribute specialized models.
Simultaneous Modeling and Multi-Team Workflows
One of the key benefits of BIM federation is simultaneous modeling, where multiple teams work on their models concurrently. This real-time collaboration allows for immediate integration and clash resolution, speeding up project timelines and improving efficiency.
Learn more about Misconceptions of BIM
Best 10 Practices: BIM Federated Project Execution

A BIM federated project involves combining multiple discipline-specific models into a unified framework to improve collaboration, accuracy, and project delivery. To maximize the benefits of BIM federation, adhering to best practices ensures smooth execution and coordination across all teams involved.
1. Clear Definition of Roles and Responsibilities
- Best Practice: Clearly define the roles of each participant, including the Lead Appointed Party, Appointing Party, BIM Manager, and other stakeholders.
2. Discipline Segregation
- Best Practice: Segregate models based on disciplines, such as architecture, structural engineering, and mechanical systems. Further, consider sub-disciplines (e.g., concrete structure models, steel structure models) for increased clarity.
3. Regular Model Coordination and Clash Detection
- Best Practice: Schedule frequent model coordination meetings to detect and resolve any clashes or inconsistencies between models using specialized BIM tools like Navisworks or BIM 360.
4. Use of Common Data Environment (CDE)
- Best Practice: Implement a CDE (Common Data Environment) to store, share, and manage all project data in one place. Platforms like BIM 360 or Autodesk Platform Services (formerly Forge) are ideal for managing document and model updates in real-time.
5. Standardized Naming Conventions and File Structures
- Best Practice: Establish standardized naming conventions and file structures across all teams. Consistent file organization, naming, and model structure ensure that models can be easily located, understood, and integrated into the federated environment.
6. BIM Protocol and Documentation Compliance
- Best Practice: Ensure all participants follow the established BIM Execution Plan (BEP) and relevant protocols, such as ISO 19650 and COBie standards. Regularly update as-built documentation to reflect project progress.
7. Simultaneous Modeling
- Best Practice: Encourage simultaneous modeling, where multiple teams (architecture, structural, MEP) work on their models concurrently rather than sequentially. Use the federated model to manage overlaps and interdependencies.
8. Continuous Collaboration and Feedback Loops
- Best Practice: Foster an environment of continuous collaboration, where feedback from all disciplines is encouraged and integrated into the federated model. Tools like BIM 360 enable teams to comment and collaborate directly on models.
9. Effective Use of Digital Twins
- Best Practice: Integrate Digital Twins into the federated model to allow real-time monitoring and simulations of building performance, asset management, and lifecycle operations.
10. Ongoing Training and Skill Development
- Best Practice: Provide ongoing training to ensure all team members are proficient with the latest BIM tools and standards. Encourage collaboration between in-house teams, task teams, and sub-consultants to improve understanding of the federated process.
Tackling Coordination Issues in Federated BIM Models
- Clash Detection:
- Use tools like Navisworks to regularly detect and resolve clashes between models (e.g., structural and mechanical systems).
- Consistent Model Updates:
- Ensure all teams update models regularly in a Common Data Environment (CDE) to avoid discrepancies.
- Clear Roles and Responsibilities:
- Define roles in the BIM Execution Plan (BEP) to prevent overlap and ensure accountability.
- Structured Communication:
- Set up communication protocols via BIM 360 for feedback and clash reports.
- Standardized Naming:
- Use consistent naming conventions and file structures for smooth integration across teams.
- Federated Model Coordinators:
- Assign coordinators to manage and oversee the integration of discipline-specific models.
- Clash Tolerance Thresholds:
- Set acceptable thresholds to prioritize critical clashes, focusing on high-priority conflicts first.
- Regular Coordination Meetings:
- Schedule frequent meetings to review models, discuss clashes, and ensure alignment.
- Simultaneous Modeling:
- Enable teams to work on models concurrently and integrate them regularly for real-time collaboration.
- Training and Skill Development:
- Offer continuous training on clash detection, coordination, and BIM tools to maintain project efficiency.
Real-World Examples
Large-Scale Projects: In complex projects involving multiple disciplines, a Federation Strategy ensures seamless integration and coordination, leading to successful project completion.
Renovation Projects: For renovation and retrofit projects, federating existing conditions with new designs helps in accurate planning and execution.
Conclusion
Using a Federation Strategy in BIM is crucial for ensuring coordination, efficiency, and quality in construction projects. At JMKON LLC, we employ this strategy to deliver projects that meet the highest standards, on time and within budget.
Adopting a Federation Strategy helps construction management companies improve collaboration, reduce costs, and achieve better project outcomes.
The Role of BIM in Construction Industry: Driving Innovation and Efficiency